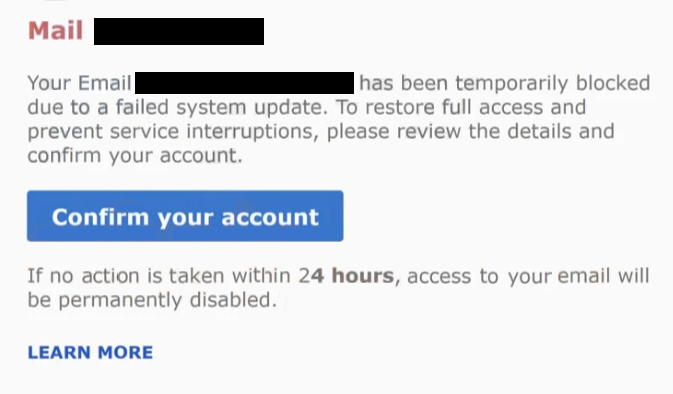
The “Failed System Update” email is a phishing attack that falsely claims a system update associated with the recipient’s email account did not complete successfully. The message is not a legitimate notification from an email provider or system administrator. Its purpose is to persuade recipients to follow a link and enter their email login details on a fake page.
The email presents itself as a technical notice and states that a recent system or security update failed. It suggests that this failure may affect email functionality, security, or account access. Rather than describing a future problem, the email implies that the issue has already occurred and requires attention to prevent further disruption.
The message does not explain what update failed, when the update was attempted, or what part of the system was affected. No version numbers, timestamps, or technical references are provided. This lack of detail is intentional. By keeping the explanation vague, the email allows recipients to assume the issue relates to their account without being able to easily verify the claim.
A link included in the email asks the recipient to resolve the problem. The wording suggests that clicking the link will allow the update to be completed or the account to be restored. Clicking the link does not lead to an official email service website. Instead, it opens a phishing page designed to look like an email sign-in or system verification screen.
The phishing page uses a simple layout with standard login fields and neutral text. It may reference system validation or update confirmation, but avoids naming a specific provider. This generic design allows the page to appear compatible with many email services. The page requests the recipient’s email address and password to proceed.
In some cases, the page asks for additional information, such as confirmation details or alternate contact information. The explanation given is that this data is required to finalise the update. Any information entered on the page is collected by the operators behind it.
After the information is submitted, the page may display a message stating that the update has been completed successfully. The session may then redirect elsewhere or close automatically. This behaviour is meant to give the impression that the issue has been resolved. No real update takes place, and the legitimate email account remains unchanged.
With valid login credentials, attackers can access the email account without the owner’s awareness. They can read messages, monitor communications, and initiate password resets for other services linked to the same email address. Because email accounts are often used for account recovery, access to one inbox can lead to access across multiple platforms.
The “Failed System Update” scam does not involve attachments, downloads, or software installation. The attack relies entirely on impersonation and routine technical language. System updates are common, and recipients may assume the email refers to a legitimate maintenance process.
The email is sent broadly and does not identify a specific email provider. This allows recipients to associate the message with whichever email account they use most often.
How to recognise phishing emails
The “Failed System Update” phishing email can be identified by focusing on what the message claims and how it asks you to respond. One of the clearest warning signs is the claim that a system update failed without any prior notice. Legitimate providers inform users about updates in advance or include clear information about what was affected.
Another sign is the lack of technical detail. The email does not explain which system was updated, what caused the failure, or how the issue was detected. Real system notifications include specific information that allows users to understand the situation.
The way the email asks you to fix the problem is also important. This message instructs you to click a link and enter your email password to resolve the issue. Email providers do not ask users to submit passwords through links in unsolicited emails. System issues are resolved after signing in directly through official websites or applications.
Sender information can also reveal problems. While the display name may look technical or system-related, the actual sender address often belongs to an unrelated domain. Checking the full sender details can expose this mismatch.
The link destination provides further clues. Hovering over the link may show a domain that does not belong to a recognised email service. Pages used in this phishing attack often rely on generic or unfamiliar domains. A secure connection indicator does not mean the page is legitimate.
The email also avoids personal details. It does not include your name, email address, or any account-specific references. Legitimate update notices usually include information that confirms the message applies to your account.
Another warning sign is the lack of other ways to check the issue. Real providers allow users to review system notices by signing in directly through their official website. This email pushes you toward a single link and does not offer independent verification.
If you have not recently received update notices or experienced service issues, an unexpected “Failed System Update” email should be treated with caution. The safest response is to ignore the link and sign in directly through your email provider’s official website. If no alert appears after signing in, the email was not legitimate.
Knowing how real email providers communicate system updates makes it easier to recognise messages like this and avoid exposing your login information.
Site Disclaimer
2-remove-virus.com is not sponsored, owned, affiliated, or linked to malware developers or distributors that are referenced in this article. The article does not promote or endorse any type of malware. We aim at providing useful information that will help computer users to detect and eliminate the unwanted malicious programs from their computers. This can be done manually by following the instructions presented in the article or automatically by implementing the suggested anti-malware tools.
The article is only meant to be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions given in the article, you agree to be contracted by the disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the artcile will present you with a solution that removes the malign threats completely. Malware changes constantly, which is why, in some cases, it may be difficult to clean the computer fully by using only the manual removal instructions.