The “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” email scam is a phishing email that claims there is a problem with the recipient’s email account because of an issue with IMAP or POP3 settings. The message states that the email server was unable to verify the account configuration and that immediate action is required to fix the problem. The email is not sent by the real email provider. It is created by scammers to steal login credentials.
In this scam, the subject line and opening text mention “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” in order to sound technical and urgent. The body of the email states that the recipient’s email client settings have failed verification on the mail server and that failure to update them will result in loss of access to incoming or outgoing emails. The wording is intended to create concern and prompt the recipient to act quickly without verifying the claim.
The message does not include specific account details from the recipient’s real email provider. It does not mention the provider’s name, the account plan, recent login activity, or any part of the email address that would prove the message is based on actual server checks. Instead, the email uses general terms such as “mail server,” “verification failure,” and “account verification”, so it can be sent to many different people using different services.
Embedded in the email is a link that the recipient is told to click in order to complete the server verification process. The link is labeled with text such as “Verify Now,” “Update Account,” or “Confirm Settings.” It is described as the location where the account can be verified and restored. The email does not instruct the recipient to sign in through the official email provider website or to navigate to the provider’s known login page. All action is funneled through this one link.
When the link is clicked, it opens a phishing page designed to mimic the login interface of an email provider. The page usually displays fields where the user is asked to enter their email address and password. In some versions of the scam, the page may ask for additional information such as recovery email addresses, answers to security questions, or other personal details that appear to be part of an account verification process.
Any information entered on this fake page is captured by scammers. The credentials are not used to fix any verification failure. Instead, the captured details are transmitted to the person or group controlling the phishing page. Scammers can then attempt to use this information to access the real email account.
Gaining access to an email account can have serious consequences. Once inside, scammers can read private messages, monitor incoming communications, and collect sensitive information such as financial details, personal contacts, and account recovery codes. Because email accounts often serve as the gateway for password resets on other online services, access to the inbox can allow scammers to take over additional accounts, such as banking, shopping, social media, or cloud storage services.
After the phishing page collects credentials, it may display a confirmation message stating that the server verification was successful or that the account has been updated. These messages are meant to reassure the victim and prevent immediate suspicion. They do not reflect any actual interaction with the real mail server.
A legitimate email provider does not resolve mail server verification issues by asking users to enter their credentials on pages reached through links in unsolicited emails. Real technical notices from service providers direct users to log in through the official website or application to view and address account issues.
The “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” email scam relies on technical-sounding language to appear convincing. It uses terms associated with standard email protocols, but the scenario it describes does not come from a real server check. The entire setup is a trick to lure recipients into entering their login details on a fake page.
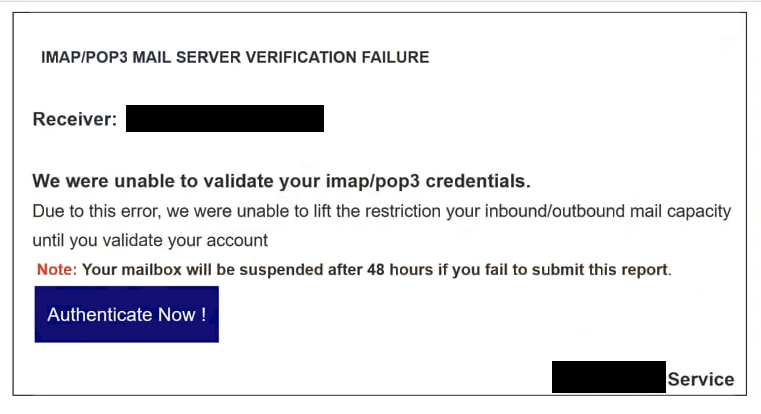
The full “IMAP/POP3 Mail Server Verification Failure” phishing email is below:
Subject: Authentication Time Our Error !
IMAP/POP3 MAIL SERVER VERIFICATION FAILURE
Receiver: ********
We were unable to validate your imap/pop3 credentials.
Due to this error, we were unable to lift the restriction your inbound/outbound mail capacity until you validate your accountNote: Your mailbox will be suspended after 48 hours if you fail to submit this report.
Authenticate Now !
How the “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” email scam is delivered and how to recognize it
The “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” email scam is sent through phishing campaigns that distribute the same or highly similar messages to large numbers of addresses. The scam does not verify whether the recipient uses a specific email service or has any server verification issues. It assumes that most people with email accounts will find the term “IMAP/POP3” familiar enough to cause concern.
One of the first signs that the email is fraudulent is the sender’s address. The display name may look official or reference a mail support team, but the actual sending domain typically does not match that of a legitimate email provider. For example, the sender address may come from a free email service or an unrelated domain. Checking the full sender address often reveals this inconsistency.
The content of the email also lacks verifiable details. The “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” scam does not include account-specific identifiers, error codes from real system logs, or context that ties the notice to actual activity on the recipient’s account. Genuine technical alerts usually include more precise information and allow the user to review details after signing in through the official provider’s platform.
The link included in the email is another strong indicator of phishing. Hovering over the link without clicking can reveal that the destination domain is not part of the legitimate email provider’s domain. Phishing links often lead to unrelated web addresses that host fake login forms. Even if the page looks convincing, the web address in the browser’s address bar shows that it is not the official site.
The fake login page used in the scam may mimic the look of a real email provider’s sign-in interface. However, the domain name and URL structure will differ from the authentic site. Any page that asks for credentials after being reached through an unsolicited email link should be treated with suspicion.
Another red flag is any request for personal information beyond normal login credentials, such as answers to security questions or recovery email addresses. Legitimate providers do not request this type of information through email links.
The “IMAP/POP3 mail server verification failure” email scam uses technical terms to create a false scenario. Recognizing signs such as mismatched sender domains, suspicious links, and requests for credentials through email links can help identify this message as a phishing attempt. Users who receive unexpected server failure notices should access their email accounts only through the official website or app to check for genuine issues. If no issues are visible there, the email should be regarded as fraudulent and deleted.
Site Disclaimer
2-remove-virus.com is not sponsored, owned, affiliated, or linked to malware developers or distributors that are referenced in this article. The article does not promote or endorse any type of malware. We aim at providing useful information that will help computer users to detect and eliminate the unwanted malicious programs from their computers. This can be done manually by following the instructions presented in the article or automatically by implementing the suggested anti-malware tools.
The article is only meant to be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions given in the article, you agree to be contracted by the disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the artcile will present you with a solution that removes the malign threats completely. Malware changes constantly, which is why, in some cases, it may be difficult to clean the computer fully by using only the manual removal instructions.