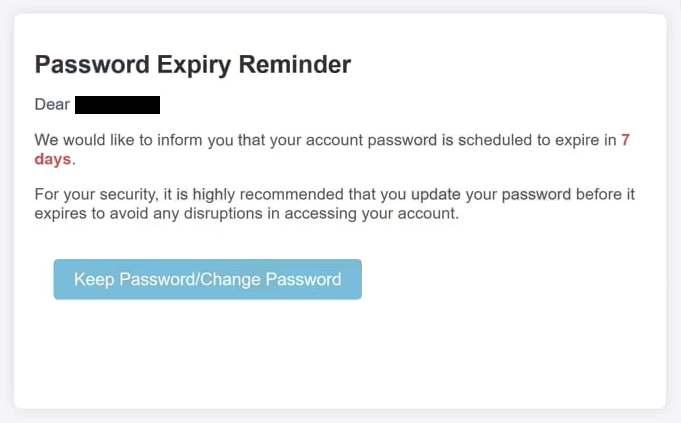
The “Password Expiry Reminder” phishing scam is an email-based attack designed to steal email account credentials by falsely claiming that a password is about to expire. The email presents itself as an official notification from an account provider or internal system and warns that continued access depends on updating the password immediately. The message is created to appear routine while creating urgency.
The email states that the recipient’s password has reached or is approaching its expiration date. It implies that failure to act will result in account disruption or restricted access. The wording suggests that the situation is time-sensitive, encouraging recipients to respond without verifying the email.
A “Keep Password/Change Password” button is included in the email, directing the recipient to update the password. Clicking this link does not open a legitimate password management page. Instead, it redirects to a phishing website designed to imitate a real password reset interface. The page uses familiar design elements such as logos, form layouts, and colour schemes associated with common account services.
On the phishing page, the recipient is prompted to enter their current email password and a new password. Some versions of the scam request additional details such as recovery email addresses or phone numbers. All entered data is collected by the attackers. The page may then display a confirmation message stating that the password has been updated or redirect the user to another page to reduce suspicion.
Once attackers obtain valid credentials, they can access the compromised account directly. This access allows them to read private messages, change account settings, or reset passwords for linked services. Because many users reuse passwords across platforms, a single phishing interaction can expose multiple accounts.
The “Password Expiry Reminder” scam does not involve attachments, downloads, or malware. Its success relies entirely on deception and familiarity. Password updates are a common and legitimate process, which makes the message appear credible. The attackers exploit this expectation to convince recipients that the email represents a routine maintenance notice.
The email is distributed broadly and does not depend on knowing whether the recipient actually uses the referenced service. The message is intentionally generic, allowing recipients to assume it applies to an account they maintain. This approach increases the likelihood of engagement.
How to recognise phishing emails that reference password expiry
Recognising phishing emails like the “Password Expiry Reminder” scam requires attention to how the message requests action. One of the clearest indicators is urgency. The email insists that the password must be updated immediately to avoid loss of access. Legitimate service providers notify users of password requirements through account dashboards and do not rely on unsolicited emails with deadlines.
The embedded link is another critical indicator. Hovering over the link often reveals a destination that does not match the official domain of the service mentioned in the email. Even when the visible text looks legitimate, the actual URL may lead to an unrelated or misleading domain.
The sender’s address should also be examined carefully. While the display name may appear official, the underlying email address often originates from a domain unrelated to the claimed provider. Checking the full sender information can reveal discrepancies that indicate impersonation.
Phishing emails referencing password expiry often lack personalised details. The message may not include the recipient’s name, account identifier, or service-specific information. Authentic password notifications usually reference identifiable account details or direct users to log in through established channels.
The content of the email is another clue. Phishing messages tend to remain vague about why the password is expiring and do not explain how the policy applies. Legitimate notifications provide clear instructions and direct users to access account settings independently.
Requests to enter passwords through email links are a definitive red flag. Service providers do not ask users to submit passwords or security details through links received via unsolicited emails. Password updates are completed after signing in through official websites or applications accessed directly.
Formatting and language inconsistencies may also be present. Even well-crafted phishing emails can include unusual phrasing, inconsistent branding, or layout differences that do not match official communications.
Recipients should also consider context. If there has been no recent login, no password policy notification, or no account interaction suggesting expiration, an unexpected reminder should be treated with caution.
The safest response is to avoid clicking any links in the email. Users should manually navigate to the service provider’s official website and check account settings directly. If no password action is required after signing in, the email was not legitimate.
Understanding how legitimate password management works helps users identify phishing attempts that rely on familiarity rather than accuracy. By verifying account status independently, users can avoid credential theft and protect their accounts from unauthorised access.
Site Disclaimer
2-remove-virus.com is not sponsored, owned, affiliated, or linked to malware developers or distributors that are referenced in this article. The article does not promote or endorse any type of malware. We aim at providing useful information that will help computer users to detect and eliminate the unwanted malicious programs from their computers. This can be done manually by following the instructions presented in the article or automatically by implementing the suggested anti-malware tools.
The article is only meant to be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions given in the article, you agree to be contracted by the disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the artcile will present you with a solution that removes the malign threats completely. Malware changes constantly, which is why, in some cases, it may be difficult to clean the computer fully by using only the manual removal instructions.