Lazarus group, the notorious hacking group with ties to the North Korean goverment, is reportedly using a new multi-platform malware framework, dubbed MATA, to target corporate networks around the world. Lazarus group has been been active for many years, they first gained worldwide attention for hacking Sony Films in 2014 and then for being behind the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack. But they have been targeting countries for far longer than that. Financial organizations in countries like India, Mexico, South Korea, Vietnam, Chile have been targeted in the past, as well as goverment, media, and technology sectors. This advanced MATA malware framework is the newest tool Lazarus used to target various entities.
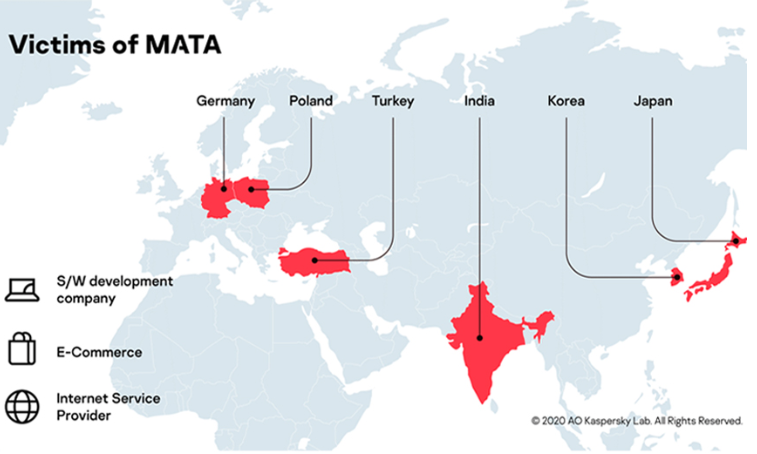
MATA was recently spotted by Kaspersky Lab’s Global Research and Analysis Team, and it appears that it was used to attack corporate entities in countries such as Germany, Poland, Turkey, India, Korea, and Japan. Targeted companies include a software development and an e-commerce companies, as well as an internet service provider, that manage a lot of data, and that’s why using a web scraping tool could be essential for this purpose.
“Based on our telemetry, we have been able to identify several victims who were infected by the MATA framework. The infection is not restricted to a specific territory. Victims were recorded in Poland, Germany, Turkey, Korea, Japan and India. Moreover, the actor compromised systems in various industries, including a software development company, an e-commerce company and an internet service provider,” Kaspersky said.
MATA malware framework was used in attempts to steal customer databases
The MATA malware framework has many features that can perform a variety of different malicious activities on an infected device, and can target Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems. When executing an attack, malicious actors may use MATA to manipulate files and system processes, inject DLLs and create HTTP proxies.
According to Kaspersky, who released an extensive report about this, MATA-related artefacts were first used around April 2018. It was aggressively used to infiltrate corporate entities all over the world.
“The first artefacts we found relating to MATA were used around April 2018. After that, the actor behind this advanced malware framework used it aggressively to infiltrate corporate entities around the world,” Kaspersky’s report says.
While the full intentions of Lazarus can only be guessed, it’s pretty clear that one of their interests is customer databases. Kaspersky noticed that in one case where MATA and its plugins were deployed, the malicious actors operating it tried to find the victim’s database and execute several database queries to steal the customer list, though it is not known whether they were successful. Distributing ransomware may also be one of its purposes, as it was used to infect a victim with VHD ransomware in one particular case.
Kaspersky has linked MATA to Lazarus group based on unique orchestrator file names that were also noticed in versions of the Manuscrypt trojan, which is known to be a tool used by North Korean hackers.
“Moreover, MATA uses global configuration data including a randomly generated session ID, date-based version information, a sleep interval and multiple C2s and C2 server addresses. We’ve seen that one of the Manuscrypt variants (ab09f6a249ca88d1a036eee7a02cdd16) shares a similar configuration structure with the MATA framework,” Kaspersky added.
Kaspersky anticipates that the malware will evolve in the future.